|
|
Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis
Primary Pneumatosis Intestinalis
General Considerations
- Gas in the bowel wall
- Occurs as a primary and secondary forms
- Primary form is uncommon and is also called pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis
- Secondary form (85%) occurs with
- Necrotizing GI diseases
- Immunosuppression
- Transplantation including bone marrow transplants
Clinical Findings
- Primary form is asymptomatic
- Symptoms of secondary form will depend on the cause
Imaging Findings
- Primary form
- Multiple, thin walled submucosal or subserosal cysts containing air
- Air content is high in hydrogen
- Occurs mostly in sigmoid and descending colon
- May mimic polyps when they protrude into lumen on BE or endoscopy
- CT is diagnostic
- Secondary form

- More common in small intestine
- Linear and streak-like rather than cystic
- Parallels bowel wall
Differential Diagnosis
- Stool may mimic the appearance of pneumatosis on conventional radiographs
- CT will show air in bowel wall on dependent surface in pneumatosis
- Air in the lumen should rise to the highest non-dependent part of lumen
Treatment
- None is usually needed for primary form
Prognosis
- Depends on cause
- Ominous in mesenteric ischemia
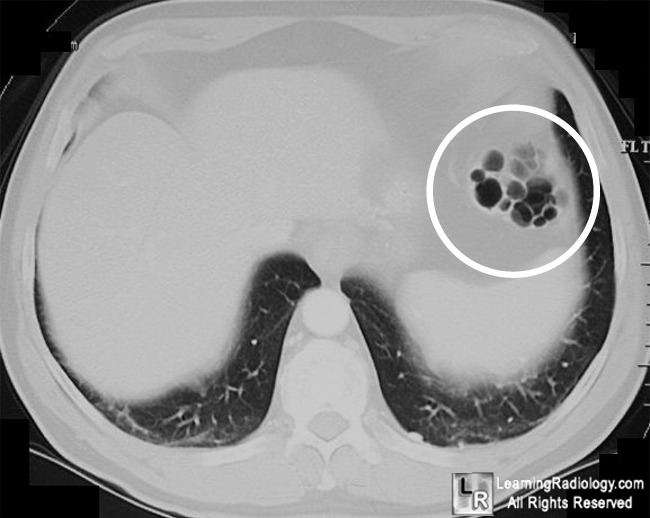 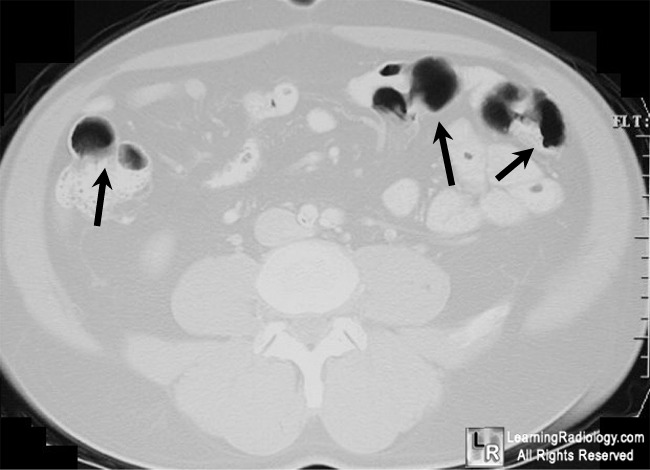
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Air-containing, cystic lucencies
are seen in bowel wall in proximal descending colon (white circle) and in the wall of
the large bowel in the lower abdomen (black arrows). The shape, density and location are characteristic for pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis.
For more information, click on the link if you see this icon 
For these same photos without the arrows, click here and here
eMedicine Pneumatosis Intestinalis Goyal, S; Weltman, D and Balsam, D
|
|
|